The Comprehensive Guide to Grain Drying: Techniques, Benefits, and Importance in Agriculture
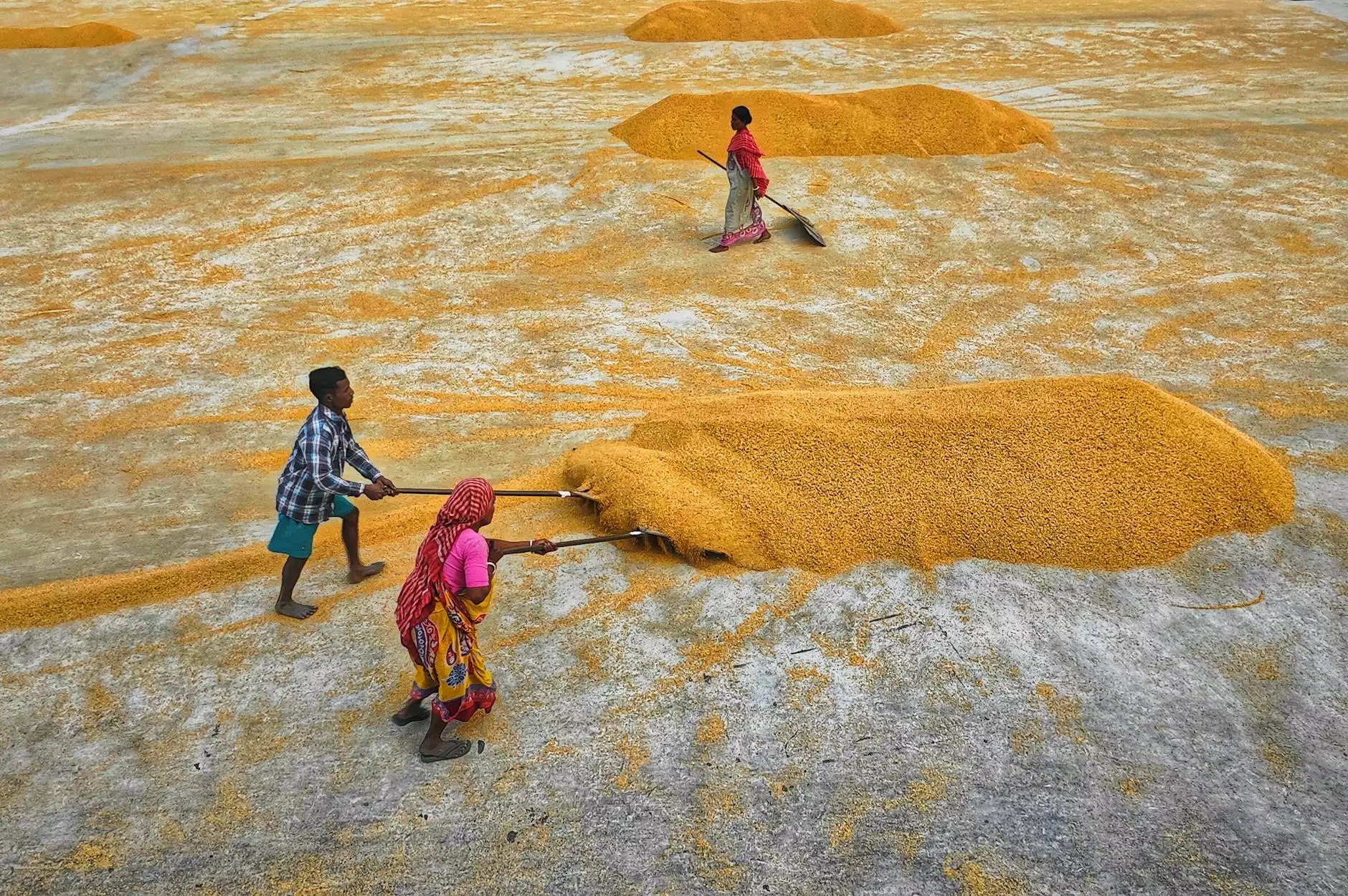

Grain drying is a critical process in the agricultural sector, vital for ensuring the quality and longevity of harvested crops. As moisture accumulation can lead to spoilage and decreased market value, understanding the fundamentals of grain drying is essential for farmers and agricultural operators. This comprehensive guide will explore the various techniques, benefits, and the significant impact of grain drying in modern farming.
Understanding Grain Drying
Grain drying involves reducing the moisture content of harvested grains to safe levels for storage and transport. High moisture content can lead to several issues, including:
- Mold Growth: Excess moisture fosters mold and fungal growth, which can render grain unfit for consumption.
- Pest Infestation: Damp grains attract insects and rodents, further compromising the quality.
- Decreased Quality: Moisture can lead to a decline in the nutritional value and flavor of the grain.
The standard moisture content for safe storage varies depending on the type of grain but usually ranges between 12% to 14%. Farmers must monitor moisture levels closely during harvest time to avoid these issues.
Importance of Grain Drying in Agriculture
Grain drying plays a pivotal role in agricultural success for several reasons:
1. Enhancing Shelf Life
By reducing moisture content, grains can be stored for extended periods without degrading in quality. This is especially important for grains intended for sale in distant markets or for use throughout the year.
2. Improving Marketability
Farmers who practice effective grain drying are able to offer their products at higher quality standards, which can lead to better pricing and greater customer satisfaction.
3. Preventing Waste and Loss
Investing in grain drying technology can significantly minimize potential losses associated with spoilage and pest damage, ultimately protecting the farmer’s financial investment.
4. Meeting Regulatory Standards
Many markets have stringent guidelines concerning moisture levels in grains. Adequate drying ensures compliance with these regulations, eliminating the risk of fines or rejected shipments.
Techniques of Grain Drying
There are several methods employed for grain drying, each with distinct advantages and considerations:
1. Air Drying
Air drying is one of the simplest methods, relying on natural airflow and sun exposure. While this method is cost-effective, it is highly dependent on weather conditions, making it less reliable in humid or rainy climates.
2. Mechanical Drying
Mechanical drying involves using specialized equipment to remove moisture quickly and efficiently. There are various types of mechanical dryers:
- Continuous Flow Dryers: Suitable for large-scale operations, these dryers process grain continuously, providing uniform drying.
- Batch Dryers: Used for smaller quantities, these systems dry a set amount of grain and require manual intervention to load and unload.
Mechanical drying offers additional control over the drying process, allowing for optimal moisture levels to be achieved regardless of external conditions.
3. Solar Drying
Utilizing solar energy for grain drying combines sustainability with cost-efficiency. Solar dryers harness heat from sunlight to evaporate moisture. While they are eco-friendly, their efficiency can be impacted during rainy seasons.
4. Chemical Drying
In some cases, chemical agents can be used to absorb moisture from grains. This method can be effective but typically requires careful handling and knowledge of the chemicals involved.
Choosing the Right Drying Method
The selection of an appropriate grain drying method depends on several factors, including:
- Scale of Operation: Larger farms may benefit from mechanical drying solutions, while smaller operations might opt for air or solar drying.
- Cost Considerations: Farmers must evaluate both initial investments and operational costs when selecting a method.
- Climate Conditions: In regions with high humidity, mechanical dryers may be necessary to ensure timely drying.
Best Practices for Effective Grain Drying
To maximize the benefits of grain drying, farmers should adhere to several best practices:
1. Timely Harvesting
Harvesting grains at the right moisture levels is crucial. Waiting too long can increase moisture absorption from rain or dew, complicating the drying process.
2. Monitor Moisture Levels Regularly
Investing in a reliable moisture meter can help farmers keep track of moisture levels throughout the drying process, ensuring they meet the ideal range for storage.
3. Maintain Equipment Efficiently
Whether using mechanical dryers or other equipment, regular maintenance is essential to ensure optimal performance and prevent malfunctions.
4. Store Grains Properly Post-Drying
Once grains are dried, they should be stored in a cool, dry place to prevent reabsorption of moisture. Proper sealing and storage practices can further protect the grain's quality.
Investing in Grain Drying Technology
Adopting modern grain drying technologies can significantly enhance efficiency and productivity. As agriculture evolves, farmers are encouraged to explore innovative solutions such as:
- Automated Drying Systems: These technologies offer real-time monitoring and automated adjustments to optimize drying conditions.
- Energy-Efficient Dryers: Investing in energy-efficient models can reduce operational costs and improve sustainability.
- Remote Monitoring Tools: Utilizing IoT technology for remote monitoring can empower farmers to manage the drying process from anywhere, ensuring timely interventions.
The Future of Grain Drying
As climate change impacts weather patterns, the techniques and technologies for grain drying must adapt to meet new challenges. Future trends may include:
- Sustainable Practices: An increasing focus on sustainability will propel the development of eco-friendly drying methods.
- Data-Driven Decisions: The integration of big data analytics will enable farmers to make informed decisions regarding moisture management and drying processes.
- Smart Technology: Advances in technology, such as AI and machine learning, will revolutionize the grain drying industry by streamlining operations and enhancing accuracy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, grain drying is an indispensable practice for farmers looking to maintain the quality, safety, and profitability of their crops. Understanding the various drying methods, applying best practices, and investing in modern technology can significantly enhance agricultural efficiency. As the agriculture landscape continues to evolve, prioritizing effective grain drying will be key to sustaining productivity and ensuring that quality grains reach consumers worldwide. For more information on grain drying and essential farming practices, visit tsgcinc.com.